In today’s fast-paced digital world, web applications must deliver seamless, interactive, and real-time experiences. Users expect websites and apps to respond instantly, whether it’s a live chat, a stock market dashboard, or a collaborative document editor. Two major techniques that enable dynamic, asynchronous communication between clients (browsers) and servers are AJAX and Comet. While both aim to improve user experience by updating content without reloading the page, they operate differently.
AJAX is client-driven, sending requests whenever updates are needed, whereas Comet is server-driven, keeping connections open so the server can push updates instantly. Understanding these methods, their benefits, limitations, and ideal use cases is crucial for developers designing responsive and efficient applications. This guide breaks down Comet and AJAX, compares them, explains performance considerations, and provides practical advice to help you make informed choices for modern web development.
What is AJAX?
AJAX, short for Asynchronous JavaScript and XML, is a technique that allows web pages to communicate with servers asynchronously. Instead of reloading the entire page when you need new information, AJAX lets your web application send a background request to the server, fetch the data, and update only a part of the page.
Modern web applications usually use JSON instead of XML because it is lightweight and easy to parse. AJAX uses the browser’s built-in tools, like the XMLHttpRequest object or the newer fetch() API, to send requests and handle responses. This makes applications faster and reduces bandwidth usage compared to full page reloads.
How AJAX Works
-
The user performs an action on the web page, like clicking a button or typing in a search box.
-
AJAX sends a request to the server in the background without disrupting the current page.
-
The server processes the request and sends data back.
-
The client-side code updates the specific part of the page using the received data.
Common Use Cases
-
Autocomplete search boxes
-
Dynamic form submissions
-
Updating parts of a web page, like feeds or tables
-
Loading new messages or posts dynamically
AJAX is simple to implement, works with almost all modern browsers, and is ideal for applications where updates are driven primarily by user actions rather than continuous real-time events.
What is Comet?
Comet is a web programming model that allows servers to push data to clients in real-time. Unlike AJAX, where the client initiates requests, Comet keeps a connection open, enabling the server to send data whenever new information is available.
Comet is also referred to as Reverse AJAX, HTTP Streaming, or Long Polling, depending on the implementation method. This technique is widely used in applications that require low-latency updates.
How Comet Works
-
The client sends an initial HTTP request to the server.
-
The server keeps the connection open without immediately responding.
-
When new data becomes available, the server sends it through the same connection.
-
The client processes the data and often reopens the connection for continuous updates.
Common Use Cases
-
Live chat applications
-
Real-time notifications
-
Online multiplayer games
-
Collaborative editing tools
-
Stock price or activity dashboards
Comet allows data to flow instantly from server to client, making it perfect for real-time applications. However, it requires careful server management because long-lived connections can consume more resources than traditional short-lived AJAX requests.
Key Differences Between Comet and AJAX
| Feature | AJAX | Comet |
|---|---|---|
| Who initiates communication | Client | Server |
| Connection type | Short, one-off requests | Persistent or long-held |
| Ideal use case | User-triggered updates | Real-time server updates |
| Latency | Depends on polling interval | Almost instantaneous once connected |
| Server resource usage | Low | Higher, needs more management |
| Implementation complexity | Easy | Complex |
| Suitability for real-time updates | Limited | Excellent |
Client-Pull vs Server-Push
-
AJAX relies on the client repeatedly asking for new information (polling). This works well for many standard applications but can be inefficient for high-frequency updates.
-
Comet allows the server to push updates immediately, eliminating unnecessary requests and providing faster user experiences.
Performance Considerations
AJAX
AJAX sends separate requests for each update, which simplifies scaling and reduces server complexity. It’s efficient for occasional updates but can become less optimal if near real-time updates are needed. High-frequency polling increases server load and can affect performance.
Comet
Comet keeps connections open, which improves latency and provides real-time updates. However, it uses more server resources because each client maintains an open connection. For large-scale applications, developers must optimize the server to handle thousands of concurrent connections efficiently.
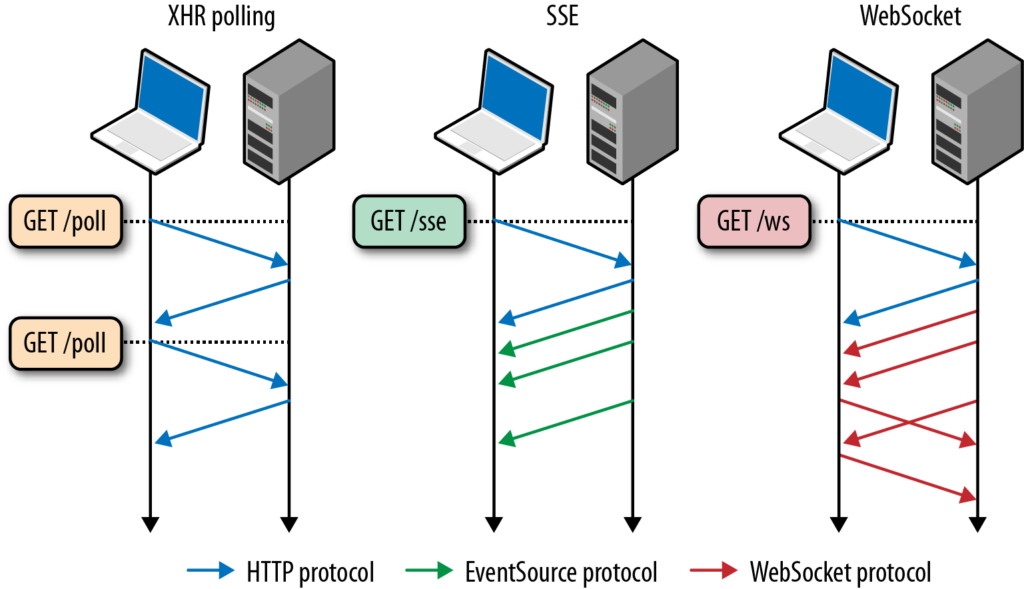
Modern alternatives, like WebSockets and Server-Sent Events (SSE), often replace Comet in new applications because they offer full-duplex communication and easier scalability. However, understanding Comet is essential for legacy systems and grasping the fundamentals of server push techniques.
Advantages and Disadvantages
AJAX Advantages
-
Simple to implement
-
Works across all browsers
-
Reduces full page reloads
-
Efficient for user-driven updates
AJAX Disadvantages
-
Not ideal for real-time server updates
-
Frequent polling can increase server load
Comet Advantages
-
Real-time server-to-client updates
-
Reduces unnecessary polling
-
Low latency for continuous data
Comet Disadvantages
-
More complex to implement
-
Higher server resource usage
-
Can be challenging to scale
When to Use AJAX vs Comet
-
Use AJAX if your application updates content based on user actions, such as form submissions, searches, or dynamic page sections, where real-time updates are not critical.
-
Use Comet if your application requires instant server-to-client communication, such as in live chat, collaborative editing, or real-time notifications.
For modern applications, combining AJAX with WebSockets often provides the best balance of ease-of-use, scalability, and real-time responsiveness.
Best Practices for Implementation
-
Optimize AJAX requests: Only request the data you need to reduce bandwidth and improve performance.
-
Manage Comet connections carefully: Use connection pooling or server optimizations to handle multiple clients efficiently.
-
Fallback mechanisms: If using Comet, consider fallback to AJAX polling for browsers or networks that do not support persistent connections.
-
Use JSON: JSON is lightweight, easy to parse, and widely supported, making it ideal for data exchange.
-
Test under load: Especially for Comet, ensure the server can handle high numbers of concurrent connections without performance degradation.
Read More: Cangshan vs Henckels: Choosing the Perfect Kitchen Knife
Conclusion
Choosing between Comet and AJAX depends largely on your application’s requirements. AJAX remains the standard for asynchronous, client-driven updates, providing simplicity, low server overhead, and improved user experience without full page reloads. It’s ideal for most interactive web pages where real-time latency is not critical. Comet, on the other hand, excels in scenarios where instant server-to-client communication is essential, such as live chat applications, collaborative editing, and notifications. While Comet offers lower latency, it requires careful server resource management and a more complex setup.
Modern alternatives, like WebSockets or Server-Sent Events, often build upon the principles introduced by Comet. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each technique, developers can deliver responsive, efficient, and highly interactive web applications that meet user expectations in today’s fast-paced digital world.
FAQs
-
What is the main difference between AJAX and Comet?
AJAX pulls data from the server when requested by the client, whereas Comet allows the server to push data to the client in real-time. -
Can AJAX be used for real-time updates?
Yes, through frequent polling, but it is less efficient and slower than server-push methods like Comet. -
Is Comet still relevant today?
While Comet concepts are still important, modern real-time applications often use WebSockets or Server-Sent Events. -
Which is easier to implement, AJAX or Comet?
AJAX is simpler and requires minimal server configuration, while Comet involves managing long-lived connections and more complex server logic. -
What are typical use cases for Comet?
Live chat apps, real-time dashboards, notifications, online gaming, and collaborative editing tools benefit most from Comet or server-push techniques.